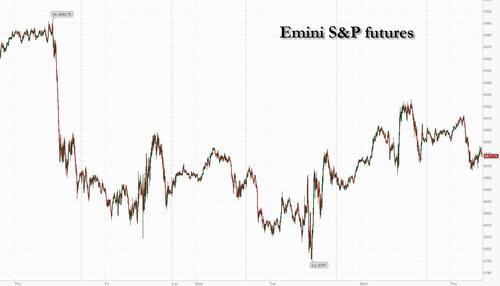
Futures Slide As Iran War Risks Add To Growing AI Disruption Fears; Oil Surges
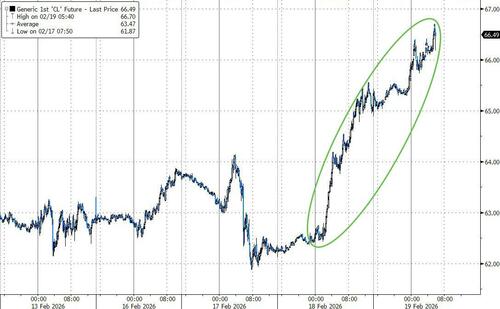
Equity futures and global markets are lower, ending a modest rebound in US stocks as concerns about a possible war with US and simmering angst over AI dent the fragile optimism seen on Wednesday. Oil extended its rally after its best day since 2021. Tech and small caps underperform which to JPMorgan's market intel desk "feels more like profit-taking and position squaring as US / Iran tensions spike with Trump saying a deal is preferred but that a strike may occur as soon as this weekend." As of 8:00am ET, S&P futures are down 0.2%, erasing an overnight gain, while Nasdaq futures drop 0.3%, with premarket weakness across all sectors ex-Energy and Aerospace/Def and tech came under renewed pressure; most Mag 7 members dropped in premarket trading. Futures dropped after the head of the UN nuclear watchdog warned that Iran’s window for diplomacy is at risk of closing. As for AI, IG’s chief market analyst Alexandre Baradez says there “seems to be no long-short strategy at play,” with hyperscaler capex and disruption to software firms both causing concern. WTI crude continues to rise and is trading at $66 after it added $2.86 /+4.6% yesterday, its strongest day since 2021. At some point Trump will have to decide if he wants war with Iran or risk soaring gas prices into the midterms. Treasuries extended their slide, pushing yields higher by 1-2bps, while the dollar was flat. Gold erased an advance above $5,000 an ounce. Today’s macro data focus is on Jobless data and the Leading Index
In premarket trading, Mag 7 stocks are mostly lower (Microsoft +0.3%, Amazon -0.2%, Alphabet -0.2%, Nvidia -0.2%, Apple -0.4%, Meta Platforms -0.5%, Tesla -0.6%)
- Avis Budget (CAR) falls 16% after the car-rental company forecast adjusted Ebitda for 2026 that missed the average analyst estimate.
- Carvana (CVNA) plunges 11% after rising costs at the online used-car retailer hit margins. Analysts flag weak retail gross profit per unit.
- Cheesecake Factory (CAKE) falls 5% after the restaurant chain’s comp sales during the fourth quarter came in below the average analyst estimate.
- Chewy (CHWY) rises over 3% after Raymond James upgraded to outperform, citing the attractive risk/reward created by recent stock weakness.
- Deere (DE) is up 6% after the company boosted its annual profit outlook as the farm-machinery maker anticipates the agriculture economy will get better soon.
- DoorDash (DASH) rises 9% after the food-delivery company issued a first-quarter orders growth forecast that topped estimates. Evercore ISI notes that fundamentals are improving and that the management’s commentary helped alleviate some investor concerns.
- EPAM Systems (EPAM) slumps 17% after the IT services company forecast its FY revenue growth rate below Wall Street expectations.
- Fiverr International (FVRR) slips 2% after receiving several analyst downgrades, with firms seeing a weaker outlook for the freelance-services marketplace in the wake of its results.
- Herbalife (HLF) rises 12% after the nutrition company said football star Cristiano Ronaldo had invested $7.5 million and provided sponsorship rights for a 10% equity stake in HBL Pro2col Software.
- Hims & Hers Health (HIMS) rises 5% after the telehealth company agreed to acquire Eucalyptus, a digital health company, for up to $1.15 billion.
- Occidental (OXY) climbs 5% after the exploration and production company gave 2026 capital expenditure guidance that was lower than expectations.
- ProPetro (PUMP) rises 3% after the fracturing company reported fourth-quarter earnings that beat the average analyst estimate and grew its contracted power capacity.
- Remitly (RELY) climbs 22% after the international money transfer service provider reported results and issued a forecast that topped analyst expectations.
- Walmart Inc. (WMT) slips 3% after issuing a forecast for full-year earnings that missed higher expectations, flagging the unpredictable state of trade and labor market conditions.
- Wayfair (W) falls 6% after the ecommerce firm reported fourth quarter results.
In corporate news, OpenAI is said to be close to securing the first phase of funding likely to bring in more than $100 billion. Samsung is looking to price its latest AI HBM4 chip up to 30% higher than the previous generation, according to local media. The CEO of Google DeepMind warned about AI risks and called for global cooperation.
What started off a solid overnight session promptly reversed just around the time Europe opened when futures tumbled into the red after the head of the United Nations nuclear watchdog warned that Iran’s window for a diplomatic deal on its atomic program is closing. Brent rose above $71 a barrel, while West Texas Intermediate was near $66. The risk of conflict in the Middle East has emerged as a new worry for traders after technology stocks drove sharp swings in recent weeks.
Brent rose above $71 a barrel, while West Texas Intermediate was near $66. Inflation concerns are already at the forefront of investors’ minds after minutes of the Federal Reserve’s January policy meeting showed several officials suggested that the central bank may need to raise rates if price growth remains stubbornly high.
Investors also remain wary of further slowing in the S&P 500’s strongest driver of the past three years, amid concerns that AI could disrupt entire sectors and that heavy capital spending wouldn’t pay off.
"What’s really interesting is that there seems to be no long-short strategy at play,” said Alexandre Baradez, chief market analyst at IG in Paris. “This will continue at least until the next earnings season when we’ll get more insight. In the meantime, all eyes will be on Nvidia’s results next week.”
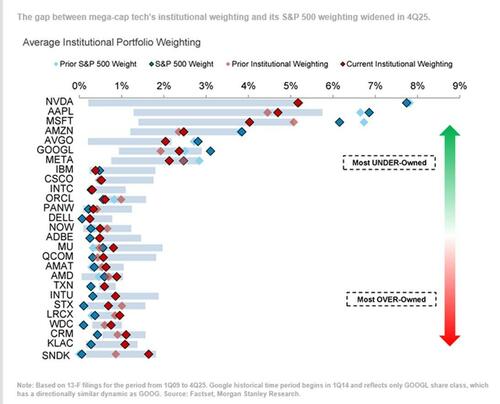
Indeed, doubts about Big Tech are playing out across the market. As we first showed here yesterday, Morgan Stanley's analysis of 13F filings shows mega-cap tech stocks finished the year the most under-owned relative to their weightings in the S&P 500 in 17 years.
And Goldman Sachs data shows 57% of large-cap mutual funds outperforming their benchmarks year-to-date, the highest share since 2007, with rotation in the equity market leading to a broadening in returns.
Simmering geopolitical risks and still-elevated tech valuations could fuel further rotation out of megacaps and into defensive sectors, said Craig Cameron, a portfolio manager at Templeton Global Investments. Still, the vast amount of capital expenditure shows that exposure to technology remains vital, he said.
“These sectors that are feeding into the AI capex cycle and the electrification cycle, those are the right places to be,” he said. “As valuations move higher, the right thing to do is to move into unloved areas and reduce that overweight over time.”
Walmart and Deere are among companies expected to report results before the market opens. Walmart results face a high bar from investors, but the main focus will be guidance and the new CEO will contend with uneven consumer sentiment, fierce competition and a lackluster US labor market. Earnings from Newmont and Copart follow later in the day.
European stocks retreated from Wednesday’s record close with the Stoxx 600 down 0.7%, after underwhelming earnings from the likes of Airbus and Renault, with investors also monitoring geopolitical risks. Nestle gained after it said sales growth would likely quicken this year. Here are some of the biggest movers on Thursday:
- FDJ United shares rally as much as 8.8%, the most since July 2024, as the lottery provider’s full-year results meet analysts’ expectations.
- Air France-KLM shares rise as much as 16% to the highest level since September, after the airline operator reported better-than-expected earnings in the fourth quarter.
- Covivio shares advance as much as 9.1%, the most since April 2025, with analysts describing the real estate investment trust’s 2025 performance as solid.
- Azelis shares rise as much as 9.6% after the Belgian chemicals distribution firm posted results which JPMorgan said represented a smaller miss than peer IMCD reported yesterday, which had caused a sharp drop in the stock.
- Tenaris shares rise as much as 6.5% in Milan, climbing to the highest since July 2008, after the steel pipe manufacturer reported robust results.
- Orange shares rise as much as 5.6% to the highest levels since 2010 as investors cheered the telecom operator’s guidance, including a lower capital spending target.
- Nestle shares rise as much as 4.5%, the most since October, after what RBC described as a “decent” fourth-quarter print from the Swiss food giant.
- Arcadis shares plunge as much as 21%, crashing to a 2021 low, after the provider of consulting and engineering services reported earnings that were well below expectations and issued guidance that analysts at Jefferies say will significantly reduce expectations for this year.
- Aegon shares drop as much as 6.8%, the most in two months, after the Dutch insurance group reported a mixed set of earnings and failed to provide an update on its UK strategic review.
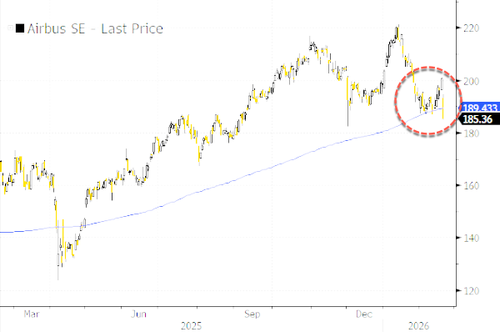
- Airbus shares fall as much as 5.9% after the French airplane company forecast commercial aircraft deliveries for 2026 of about 870 planes, lower than most previous estimates.
- Rio Tinto shares decline as much as 4.4% in London, its biggest intraday drop since August, after the miner reported net debt that analysts say missed expectations.
- Euronext drops as much as 5.1% after announcing cost guidance for 2026 that’s higher than consensus expectations, overshadowing its small fourth-quarter beats.
- Centrica shares tumble as much as 9.6%, the steepest drop since July 2024, after the British energy company did not announce a new buyback in its results
Earlier in the session. Asian stocks climbed, led by South Korea. The MSCI Asia Pacific Index rose as much as 0.6%, extending gains to a second day. Samsung Electronics and Tokyo Electron were among the biggest boosts to the gauge. South Korea’s Kospi Index advanced to a fresh record as markets reopened after a three-day holiday, while benchmarks in Japan and Singapore jumped more than 1%.
In FX, the Bloomberg Dollar Spot index is a touch higher after dipping in the European morning as EUR/USD and cable briefly reclaimed 1.18 and 1.35 respectively, and USD/JPY slipped below 155. Aussie dollar is near the top of the G-10 pile following following strong jobs data overnight.
In rates, treasuries were on course for their longest losing streak in a month as tensions in the Middle East fuel oil-driven inflation fears. The 10-year yield rose for a third day, up one basis point to 4.09%. Treasury hold small losses into the Thursday open, with yields 1bp to 2bp cheaper across a slightly steeper curve, partially unwinding this week’s flattening trend. Oil prices, up 1.6% near high end of range since August on growing tensions between the US and Iran, add to upside pressure on Treasury yields via increased inflation expectations. US 10-year yield is less than 1bp higher on the day near 4.095% after topping 4.10% for first time this week; German and UK counterparts see steeper increases, adding to pressure on Treasuries. Treasury plans $9 billion 30-year TIPS new issue auction at 1pm New York time. Focal points of US session include weekly jobless claims, 30-year TIPS auction and several Fed speakers.
In commodities, oil has continued its climb with Brent making its way onto a $71/bbl handle as Iranian conflict concerns continue to support prices. Axios reported on Wednesday that a major US military operation in the Middle East could begin soon. Upside in energy is supporting global bond yields. Spot gold has slipped below the $5,000 mark, still up 0.2% but lagging silver, up 1.3%. Bitcoin of course tumbles to LOD.
US economic calendar slate includes December trade balance, wholesale inventories, February Philadelphia Fed business outlook and weekly jobless claims (8:30am), and December Leading index and January pending home sales (10am). Fed speaker slate includes Bostic (8:20am), Bowman (8:30am), Kashkari (9am) and Goolsbee (10:30am)
Market Snapshot
- S&P 500 mini -0.4%
- Nasdaq 100 mini -0.5%
- Russell 2000 mini -0.5%
- Stoxx Europe 600 -0.7%
- DAX -0.9%
- CAC 40 -0.9%
- 10-year Treasury yield +1 basis point at 4.09%
- VIX +1 points at 20.66
- Bloomberg Dollar Index little changed at 1189.41
- euro little changed at $1.179
- WTI crude +1% at $65.81/barrel
Top Overnight News
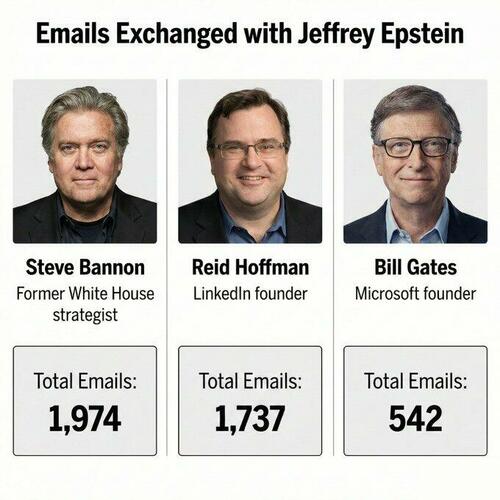
- British Police arrest King Charles' brother Andrew over misconduct relating to Epstein
- U.S. Gathers the Most Air Power in the Mideast Since the 2003 Iraq Invasion: WSJ
- The US military build-up in the Middle East means Iran’s window to reach a diplomatic agreement over its atomic activities is at risk of closing, according to the head of the United Nations nuclear watchdog. The International Atomic Energy Agency has discussed concrete proposals with Iranian Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi to inspect sites bombed last year by Israel and the US: BBG
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy says the US, and perhaps some Europeans, are discussing a new document between NATO and Russia: BBG
- OpenAI Funding on Track to Top $100 Billion in Latest Round: BBG
- Bill Gates pulls out of India AI summit amid Epstein scrutiny: RTRS
- Epstein Waged a Years-Long Quest to Meet Putin and Talk Finance: BBG
- The Bank of Japan may raise interest rates as soon as March or April, Junichi Hanzawa, chairman of the Japanese Bankers Association, says at a regular news briefing in Tokyo
- Swiss watch exports resumed their long slump in January after a brief respite the previous month triggered by the easing of US tariffs: BBG
- France’s strategy to reduce its budget deficit this year remains “very uncertain,” even after the government set less ambitious targets than initially planned, the country’s audit court said: BBG
- Walmart Sales Climb, Driven by Grocery and Online Gains: WSJ
- Walmart Cites Trade, Labor Concerns in Cautious Profit Forecast: BBG
- Top European spies sceptical US will clinch Ukraine peace deal this year: RTRS
- Top Lawyers’ Fees Have Skyrocketed. Be Prepared to Pay $3,400 an Hour: WSJ
- From Paris to New Delhi, the Push to Ban Teens From Social Media Is Going Global: WSJ
- Steve Cohen's $3.4 Billion Payday Tops Hedge Fund Ranks: BBG
- The Far-Fetched Mission to Reclaim Islands That Host a Key U.S. Military Base: WSJ
Trade/Tariffs
- US President Trump and his advisors have reportedly indicated that the USMCA could be scrapped, NY Times reports. Instead, the US could have bilateral deals with Canada and Mexico. US officials have been increasing pressure on Canada. Canadian officials cited add that their expectation for a full renewal of the USMCA is very low. Officials believe Trump is trying to weaken Canada economically to force it to give up some protectionist policies. The article reminds us that in 2018, the US proposed a bilateral deal with Mexico and told Canada to get on board or be left out.
- US-ASEAN Business Council said US and Indonesian companies signed trade and investment deals covering critical minerals, semiconductors, agriculture and forestry, while deals include a USD 4.89bln semiconductor joint venture involving Essence Global Group. Indonesian firms are to purchase 1mln tons of US soybeans, 1.6mln tons of corn, and 93,000 tons of cotton over an unspecified period.
- US President Trump posted that the US trade deficit has been reduced by 78% because of the tariffs being charged to other companies and countries, adds it will go into positive territory during this year for the first time in many decades.
- Canadian minister responsible for Canada-US trade LeBlanc said Canadian companies from various provinces have signed 15 commercial partnerships in Mexico.
A more detailed look at global markets courtesy of Newsquawk
APAC stocks traded higher following the positive handover from the US and with South Korea outperforming amid tech strength on return from the Lunar New Year holidays. ASX 200 rallied to a fresh record high with the gains led by strength in telecoms and energy, as the former was boosted alongside Telstra, which reported a 9.3% increase in H1 net profit, while energy stocks benefitted from the rise in underlying oil prices amid geopolitical frictions. Nikkei 225 gained with sentiment underpinned by a weaker currency and stronger-than-expected Machine Tool Orders. KOSPI outperformed on return from the Lunar New Year holiday closure as tech stocks played catch-up to the rebound in their US counterparts, including index heavyweight Samsung Electronics, as its shares rallied by around 5% to a record high.
Top Asian News
- Australian Unemployment Rate (Jan) 4.1% vs. Exp. 4.2% (Prev. 4.1%).
- Australian Employment Change (Jan) 17.8K vs. Exp. 20K (Prev. 65.2K, Low. -5K, High. 40K).
- Australian Part Time Employment Chg (Jan) -32.7K (Prev. 10.4K).
- Australian Full Time Employment Chg (Jan) 50.5K (Prev. 54.8K).
- Australian Participation Rate (Jan) 66.7% vs. Exp. 66.8% (Prev. 66.7%).
- Japanese Stock Investment by Foreigners (Feb/14) 1424.2 (Prev. 591.4, Rev. From 543.2).
- Japanese Machinery Orders YoY (Dec) Y/Y 16.8% vs. Exp. 3.9% (Prev. -6.4%, Low. -1.1%, High. 10.6%).
- Japanese Machinery Orders MoM (Dec) M/M 19.1% vs. Exp. 4.5% (Prev. -11.0%, Rev. From -11%, Low. 1%, High.
European bourses (STOXX 600 -0.7%) are entirely in the red. The FTSE MIB (-1.2%), DAX 40 (-0.9%) and CAC 40 (-0.8%) are the clear underperformers after a flurry of corporate news. European sectors are mixed, with a slight tilt to the downside. Food, Beverage and Tobacco (+0.7%) is outperforming following earnings by Nestle (+2.5%), which announced that it is in advanced negotiations to sell its remaining Froneri stake. At the bottom sits Basic Resources (-2.8%), Autos and Parts (-2.1%) and Utilities (-2.2%). The former continues to have a choppy week, this time catalysed by Rio Tinto (-4.6%) as FY profit failed to grow and a drag on its iron ore unit in China. For the latter, Italian utilities (A2A -3.7%, Enel -4.1%, Italgas -2.1%) have been hit after Italy approved a 2bp hike in its IRAP corporate tax. Renault (-5.9%) has been weighing on the Autos sector after posting a net loss worse than expected.
Top European News
- UK's ONS on ongoing data issues, reported the "Latest steps reaffirm commitment to quality over quantity".
FX
- DXY has waned from overnight highs after advancing yesterday and overnight amid better-than-expected data and as oil prices surged after sources noted the Trump administration is closer to a major war with Iran than people realise. On the US docket ahead, weekly initial jobless claims (which coincide with the traditional survey window for the BLS' February jobs data) are expected little changed at 225k (prev. 227k), while continuing claims (this week does not coincide with the BLS window) are seen unchanged at 1.87mln. Most recently, a NYT report suggested that the Trump administration indicated that the USMCA could be scrapped, in favour of bilateral deals with Canada and Mexico. DXY resides in a current 97.572-97.777 range at the time of writing.
- JPY is narrowly softer but off worst levels, with USD/JPY hovering around its 100 DMA (154.744), with some fleeting strength seen yesterday in wake of the FOMC minutes in which the Fed confirmed it did a USD/JPY rate check on behalf of the US Treasury in January. Analysts at ING highlight that "Something like this is extremely rare in foreign exchange markets and is a sign of a more activist White House when it comes to FX. The move was clearly designed to deliver maximum impact and reflects the shared desire from both Washington and Tokyo that USD/JPY does not sustain a move through 160".
- EUR trims some of yesterday's losses after briefly slipping beneath the 1.1800 level (to a 1.1782 low on Wednesday) as the buck strengthened, and with the single currency not helped by conflicting reports about ECB President Lagarde's future. Recent reports suggested ECB President Lagarde reportedly tells colleagues that she would tell them first if she were to step down, according to sources; colleagues reportedly interpreted this to mean her departure is not immediate, but the door is not closed. EUR/USD resides towards the top end of a 1.1781-1.1808 range.
- Antipodeans outperform amid recent underperformance and following positive risk appetite in APAC (before waning in European hours), with AUD/USD supported following the mixed jobs data, which showed headline employment change slightly missed expectations, although the unemployment rate printed lower than expected, and the increase in jobs was solely fuelled by full-time work.
Central Banks
- WSJ's Timiraos noted regarding the January Fed meeting minutes that it was interesting there was no date specified for when inflation gets to 2%, and instead minutes states that forecast is "slightly higher, on balance".
- Japan Bank Lobby said markets expect a BoJ hike as soon as March; Lobby Head believes there is a reasonable possibility of a hike as early as March or April.
- ECB President Lagarde reportedly tells colleagues that she would tell them first if she were to step down, according to sources; colleagues reportedly interpreted this to mean her departure is not immediate, but the door is not closed.
- RBNZ Assistant Governor Silk said the easing cycle is likely over and there are risks on either side, adds maintaining accommodative policy for a while aligns with economic conditions.
- SNB has defined a standardised and scalable process for the ELF that will enable participating banks to quickly obtain liquidity support against collateral as necessary.
- Riksbank takes measures to facilitate banks’ liquidity management.
Fixed Income
- USTs are lower by a handful of ticks this morning, and currently trade within a 112-24+ to 112-31 range. Moved lower for much of the morning, before picking up a touch as US/European equity futures dipped lower.
- The bearish bias follows on from; a) the prior day’s stronger-than-expected US data, b) rising energy prices (spurred by geopolitical tensions), c) JGB pressure overnight, following strong Machine Tool Orders and a weak 20yr JGB auction, d) a poor 20yr auction; on the latter point, desks highlight that the 20yr has historically not been the markets favoured outing. On the geopolitical narrative, there have been continued reports that the US is upping its presence in Iran, with a US Senior Official telling Axios that US-Iran talks have been a “nothing burger”, and that is why POTUS is close to deciding on the issue of going to war with Iran. As it stands, US paper appears to be pricing in the inflationary impacts (higher oil prices), but an outright attack could lead to some haven-related demand.
- Bunds are also pressured alongside global peers. Currently holds towards the lower end of a 129.05 to 129.31 range. Newsflow for German paper is lacking today, aside from ECB-related reporting. Source reports suggest that President Lagarde told her colleagues that she would tell them before she leaves; her colleagues reportedly interpreted this to mean her departure is not immediate, but the door is not closed. De Cos and Knot have been touted as potential replacements once President Lagarde leaves her role, though Rabobank cautions that the process is highly political and difficult to predict, noting markets should largely ignore speculation for now.
- Gilts are trading in-fitting with peers, and trading around the 92.00 mark within a 91.96 to 92.03 range. UK data slate has paused for today, ahead of Retail Sales/PMIs on Friday. This follows on from dovish jobs/wages and mixed inflation metrics earlier this week, which confirmed the disinflation process but Services and Core topped-expectations, leaving the more hawkish MPC members cautious. Markets are currently torn between a cut in March or April; analysts at ING see a cut in March and then another by June.
Commodities
- Crude benchmarks remain elevated amid heightening geopolitical tension between the US and Iran following the Axios report on Wednesday which noted that the US President Trump’s administration is closer to a major war with Iran than people realise. Tensions continue to persist, with an overnight report from CNN that the US military is ready to strike Iran as early as this weekend and the WSJ reporting that the US has gathered the greatest amount of air power in the Middle East since the 2003 Iraq invasion. WTI and Brent are trading at the upper end prices of USD 64.84-66.27/bbl and USD 70.18-71.60/bbl, respectively, with Brent touching the USD 71/bbl, which marks the first time since August last year.
- Precious metals are firmer, benefiting from haven demand from the ongoing geopolitical tension between the US and Iran, with the yellow metal crossing the USD 5,000/oz mark. The weaker USD ahead of the FOMC minutes also spurred demand for the yellow metal. XAU and XAG are trading at the upper range of USD 4979.14-5040.21/oz and USD 76.355-79.355.
- Copper price action is moving contrary to the trend seen in precious metals. Risk sentiment in the early European session as well as subdued activity from Asia due to the Chinese holiday has seen the red metal trading lower thus far. 3M LME copper trades at the lower price range of USD 12.846-12.937k/t.
- US Energy Secretary Wright said the US could leave the IEA if the group does not change.
- Hungarian PM Orban's Chief of Staff said they would take steps in the scenario that Ukraine continues to halt Druzhba oil shipments.
- US Treasury Department issues general license authorising transactions related to oil and gas sector operations in Venezuela.
- US Private Inventory Data (bbls): Crude +0.6mln (prev. +13.4mln), Distillate -1.6mln (prev. -2.0mln), Gasoline -0.3mln (prev. +3.3mln), Cushing -2.4mln (prev. +1.4mln).
Geopolitics: Ukraine
- Ukrainian President Zelensky said he is aware that the US and Europe have been talking to Russia and we must be prepared to react to surprises.
- Russia's Kremlin on the Iran situation said they see unprecedented escalation of tensions and on Ukraine talks, said there's nothing to add following comments from the likes of Medinsky yesterday. Reiterates that no date has been set for the next Ukraine talks.
Geopolitics: Middle East
- IAEA Director Grossi said Iran discussed a potential IAEA return to bombed nuclear sites, adds there is no deal unless the IAEA was in a position to verify and there is not much time to reach an Iran nuclear deal, via Bloomberg TV. His role is to get the nations into a position to come to a deal without the need for force. IAEA has proposed a few solutions.
- Russian Foreign Minister Lavrov warns of any new US strike on Iran.
- Israeli raid reported on areas of deployment of occupation forces east of Gaza City, according to Al Jazeera.
- Two Israeli defense officials said that significant preparations were underway for possibility of a joint strike with the US against Iran, according to NYT.
- US gathers the greatest amount of air power in the Middle East since the 2003 Iraq invasion and President Trump is being briefed on military options for striking Iran, even as aides hold talks with the Iranian regime, according to WSJ.
- Iraqi Foreign Minister said any alternative to US-Iran deal would be disastrous, and they may not be able to export their oil if war breaks out in the region.
- US military is ready to strike Iran as early as this weekend, although President Trump has yet to make the final decision, according to sources familiar with the matter cited by CNN.
- US senior official said US expects Iran to submit a written proposal on resolving standoff in the wake of Tuesday's talks.
Geopolitics: Others
- US is pushing NATO to cut many foreign activities, including ending a key alliance mission in Iraq, according to four NATO diplomats cited by POLITICO.
- Israeli Defense Forces announced they struck Hezbollah infrastructure sites in southern Lebanon, according to Sky News Arabia.
- US Southern Command Commander Donovan met with Venezuela's interim President Rodriguez and defence officials in Caracas.
- North Korea's Kim Yo Jong said military will take measures to strengthen its vigilance on border with South Korea; she appreciates South Korean Unification Minister's official recognition of South Korea's drone provocation. Border with the enemy should be solid.
US Event Calendar
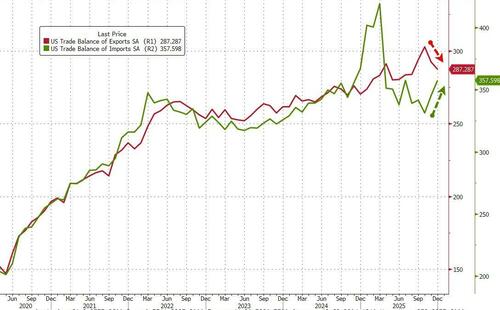
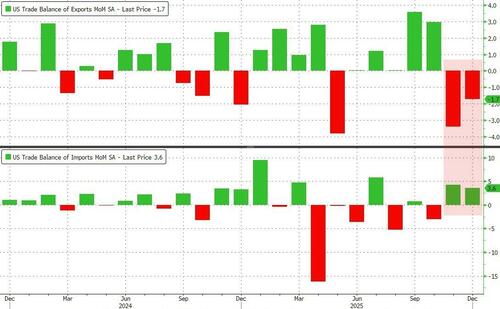
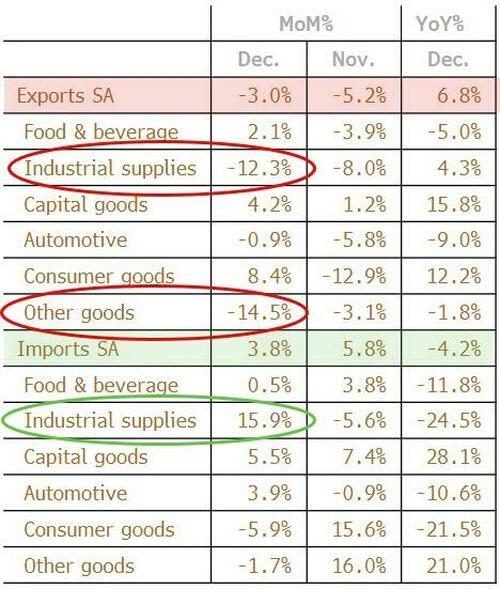
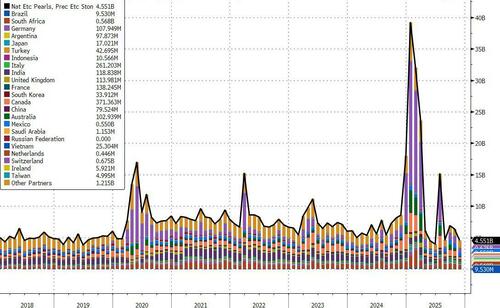
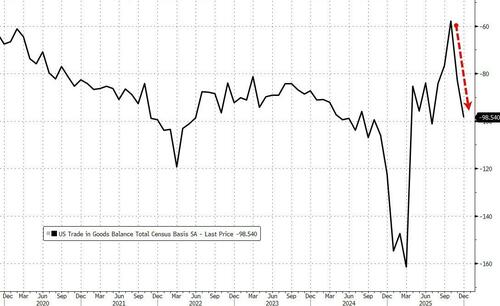
- 8:30 am: United States Dec Trade Balance, est. -55.5b, prior -56.8b
- 8:30 am: United States Dec P Wholesale Inventories MoM, est. 0.2%, prior 0.2%
- 8:30 am: United States Feb Philadelphia Fed Business Outlook, est. 7.5, prior 12.6
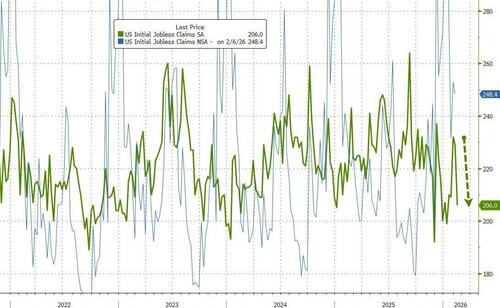
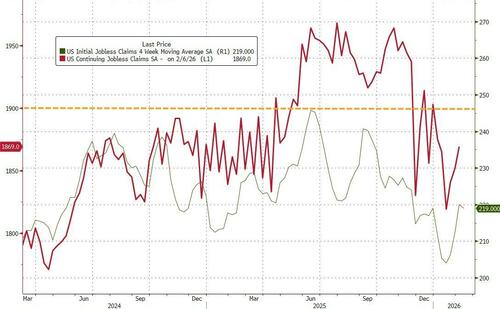
- 8:30 am: United States Feb 14 Initial Jobless Claims, est. 225k, prior 227k
- 8:30 am: United States Feb 7 Continuing Claims, est. 1860k, prior 1862k
- 8:30 am: United States Fed’s Bowman Gives Opening Remarks at Banking Conferernce
- 9:00 am: United States Fed’s Kashkari in Fireside Chat on Economic Outlook
- 10:00 am: United States Dec Leading Index, est. -0.2%, prior -0.3%
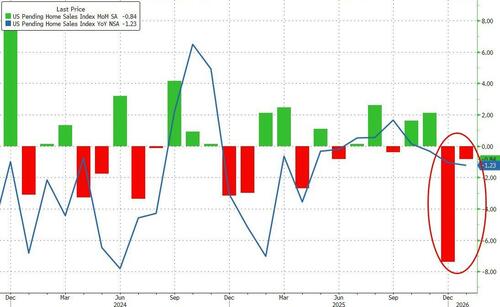
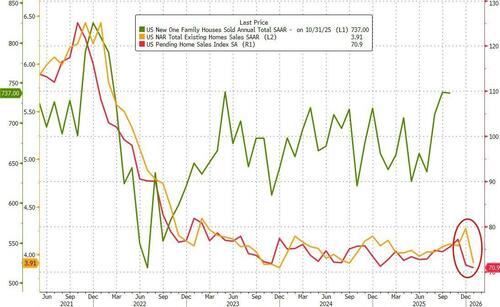
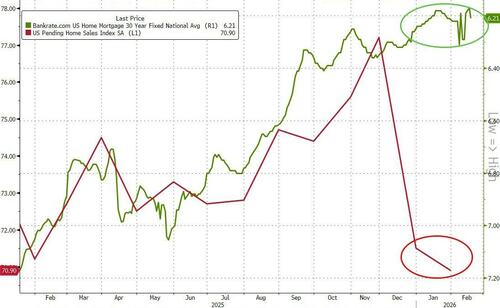
- 10:00 am: United States Jan Pending Home Sales MoM, est. 2%, prior -9.3%
- 10:30 am: United States Fed’s Goolsbee Gives Opening Remarks
DB's Jim Reid concludes the overnight wrap
The disruption narrative has taken a well-earned breather for much of this week, helping to steady nerves. Positive economic data and supportive tech news over the past 24 hours have built on that calm, pushing most major indices to solid gains. The S&P 500 advanced by +0.56%, the NASDAQ by +0.78%, while in Europe the STOXX 600 (+1.19%), FTSE 100 (+1.23%) and CAC (+0.81%) all reached new record highs. Overnight the KOSPI has reopened +2.81% higher after a 3-day break and the Nikkei (+0.78%) and Topix (+1.23%) are also higher.
Part of the catalyst for the rally were pre-US market reports that Nvidia (+1.63%) had agreed to supply Meta (+0.61%) with large quantities of processors over the coming years. The news boosted both technology and semiconductor stocks, with the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index up +0.96% and the Magnificent 7 rising by +0.77%. That said, the Magnificent 7 continues to underperform on a year to date basis (6.35%). Semiconductor sentiment was further supported by strong quarterly results and guidance from Analog Devices (+2.63%). US equity gains were also pretty broad, with almost two-thirds of the S&P 500 higher on the day, though defensive sectors including consumer staples (-0.53%) and utilities (-1.70%) underperformed.
The equity rally was reinforced by solid US economic data. January industrial production rose +0.7% m/m versus expectations of +0.4%, while factory output increased +0.6% m/m, also beating forecasts. These prints marked the biggest monthly rises in eleven months. Earlier in the morning, core capital goods shipments rose +0.9% in December (+0.3% expected), and with +0.4pp revision for the prior month. US housing starts also reached a five month high in November but that’s clearly a bit backward looking now. Next up on the data front, today’s jobless claims (215k vs. 226k) will be closely watched, given their overlap with the February employment survey period.
Treasury yields moved higher for a second day running in response to the data, with the 2yr yield up +2.7bps to 3.46% and the 10yr up +2.4bps to 4.08%. The grind higher in rates was also supported by hawkish-leaning minutes of the January FOMC meeting. Notably “the vast majority of participants judged that labor market conditions had been showing some signs of stabilization”, even though the meeting had taken place before the improved January jobs report. And “several participants indicated” support for more two-sided language on future rate moves, raising the possibility of rate hikes “if inflation remains at above-target levels”. While that’s still far from an active call to raise rates, it adds to the sense that most of the FOMC are in no rush to deliver further cuts. Overnight, US yields are up a further +1 to 1.5bps across the curve.
Elsewhere, oil rebounded sharply from Tuesday’s decline. The immediate trigger appeared to be an Axios op ed warning that the US and Iran may be moving closer to a major confrontation, though it is difficult to point to any single catalyst. More broadly, investors seem to have concluded that there has been no meaningful political breakthrough following talks earlier this week. Against that backdrop, Brent and WTI both rose by more than +4%, with Brent moving back above $70/bbl. Precious metals also recovered amid renewed geopolitical unease, with gold up +2.04% and silver jumping +5.00%. All three are edging up a little more this morning.
In Europe, front end bond yields edged higher on concerns about rising oil prices, while moves further along the curve were mixed. The 10yr bund yield was +0.1bps, while OATs (-0.6bps) and gilts (-0.2bps) edged lower. And 2yr gilts (-0.4bps) gained despite a slightly firm UK CPI print, which showed January inflation easing to +3.0% y/y from +3.4%, in line with consensus but 0.1pp above the Bank of England’s forecast. Core inflation was slightly stickier than expected at +3.1% y/y (+3.0% expected). While this does mark the lowest headline inflation in 10 months, the data could complicate the BoE’s March decision at the margin, though our UK economist still expects a cut next month given the deteriorating labour market.
Staying with Europe, the FT reported yesterday that Christine Lagarde is considering stepping down early as ECB President (as we mentioned as the story was breaking this time yesterday), ahead of the scheduled end of her term in October 2027. This potentially links to reports earlier in the week that EU leaders are discussing a package deal to fill upcoming ECB executive board vacancies at once, with Lagarde, Lane and Schnabel all due to leave during the course of 2027. A motivating factor for a possible bundling of appointments is that it would allow current European leaders to make the decision over ECB leadership, insulating it from the influence of a possible far-right French President after the next election in April 2027, especially given the RN’s past rhetoric on redefining the ECB’s mandate. Our European economists do not expect any early change in ECB leadership to significantly change the path of ECB policy going forward, with their baseline view that the ECB will keep rates on hold until mid 2027.
Other than what we discussed at the top about a rally this morning in Asia, the other story of note has been the Australian job numbers. Total employment increased by 17,800 in January, which was close to the consensus forecasts of around 20,000, but the unemployment rate surprisingly remained stable at 4.1%, a tenth below expectations. 3 and 10yr Aussie yields are +7.8bps and +6bps higher respectively. The ASX is +0.78% higher.
Looking ahead, today brings further US data including the February Philadelphia Fed business outlook, January pending home sales and initial jobless claims. Elsewhere, we’ll see France’s January retail sales, Italy’s December current account balance, Eurozone December construction output and February consumer confidence. Central bank events include the ECB’s economic bulletin and speeches from Fed officials Bostic, Kashkari and Goolsbee. Notable earnings include Walmart, Nestlé and Airbus, while the US will also auction $9bn of 30 year TIPS.
Tyler Durden
Thu, 02/19/2026 - 08:44



 DataBank’s IAD4 data center under construction in Ashburn, Va
DataBank’s IAD4 data center under construction in Ashburn, Va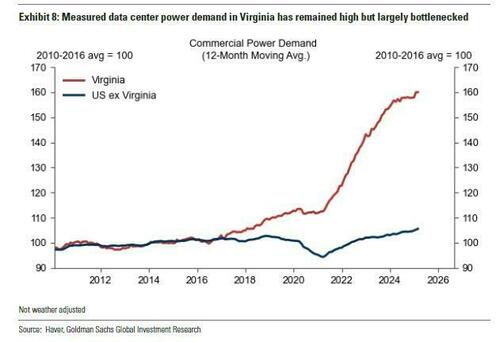






 via Associated Press
via Associated Press
Recent comments